Filestore introduction
As everybody knows, VMware ESXi can leverage NFS as its external datastore by using the NFS protocol to access and manage file-based storage, but you may not know, today, Google Cloud also officially support for Filestore as an NFS datastore for Google Cloud VMware Engine.
Google Filestore is a managed file storage service provided by Google Cloud Platform (GCP). It allows users to create and manage fully managed NFS file shares in the cloud. With Filestore, users can easily set up and manage file storage for their applications running on GCP, and it is particularly useful for workloads that require shared file access and need a high level of data consistency.
In my another blog, you can learn how VMs in GCVE can mount NFS file systems using the Firestore service. Today, let’s explore how GCVE ESXi servers can also utilize Firestore NFS as their external datastore to scale storage resources within the GCVE cluster.
Google Cloud VMware Engine currently offers the following vSphere storage options as its external datastore options:
- VMware vSAN (built-in comes with each VMware Engine node)
- External NFS storage
- Filestore High Scale or Enterprise tier instances
- NetApp Cloud Volume Service
Below is a high-level architecture diagram of how GCVE can use Filestore instances as its external datastore:
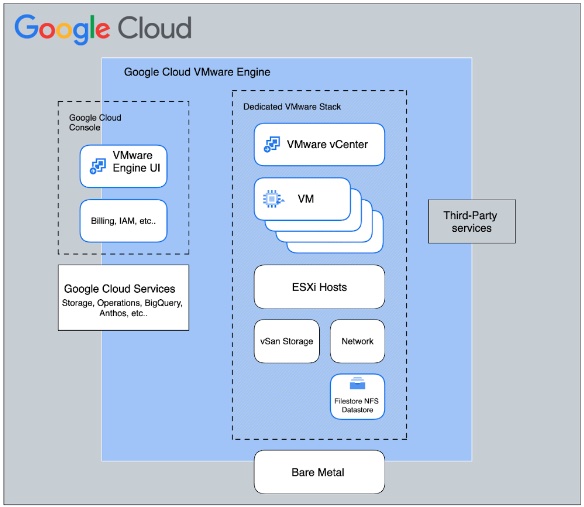
When you leverage external NFS datastores in GCVE, you have the exceptional ability to scale your storage independently of compute, making it an ideal solution for virtually all VMware workloads, with the exception of the most latency-sensitive ones (typically those requiring less than 2ms response time).
The solution described here enables VMware-certified Filestore High Scale/Enterprise NFS storage to be used as an external datastore for ESXi hosts in GCVE. It does so by enabling users to create Filestore High Scale/Enterprise instances in all regions and subsequently mount them as external data stores to their ESXi hosts in GCVE.
As of this blog post (2Q2023), the following limitations apply by this Google official documentation:
- Available only for Filestore High Scale and Enterprise tier instances. (Basic SSD and Basic HDD tier instances are not supported.)
- Crash-consistent snapshot support available in Filestore Enterprise tier instances only.
- Backup support available for both High Scale and Enterprise tiers.
- Copy offload (VAAI) is not available.
- Only NFSv3 protocol is supported.
- Not yet accessible via GCVE UI/API/CLI in this release and users need to file support tickets for mounting/unmounting of datastores backed by external Filestore instances.
Configuring steps
Below are the steps required for this integration:
Create Filestore instance
You can create Filestore instances, and manage those instances using the Google Cloud console, you can see I have already created a “gcve-filestore” instance in asia-northeast1 region, which is the “Enterprise” service tier.

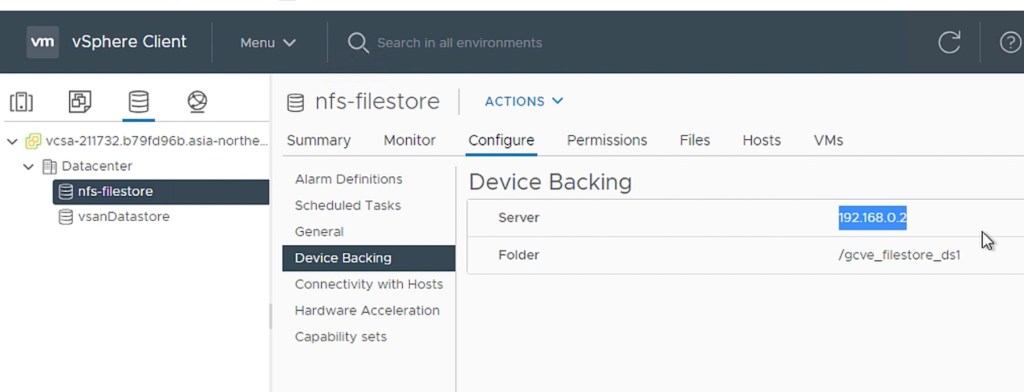
The NFS has a capacity of 1TB and its IP address is 192.168.0.2. The NFS mount point is “192.168.0.2:/gcve_filestore_ds1”.

Configure service subnet in GCVE
When you create a private cloud, VMware Engine creates additional service subnets (service-1, service-2, service-3, service-4, service-5). Service subnets are targeted for appliance/service deployment scenarios, such as storage, backup, DR, media streaming, providing high scale linear throughput and packet processing for even the largest scaled private clouds. VM communication across a service subnet exits the VMware ESXi host directly into the Google Cloud networking infrastructure empowering high speed communication.
Service subnets have no CIDR allocation on initial creation. You must specify a non overlapping CIDR range and prefix for this integration. You need to assign a /24 CIDR for the GCVE service network that will be used for external NFS storage.
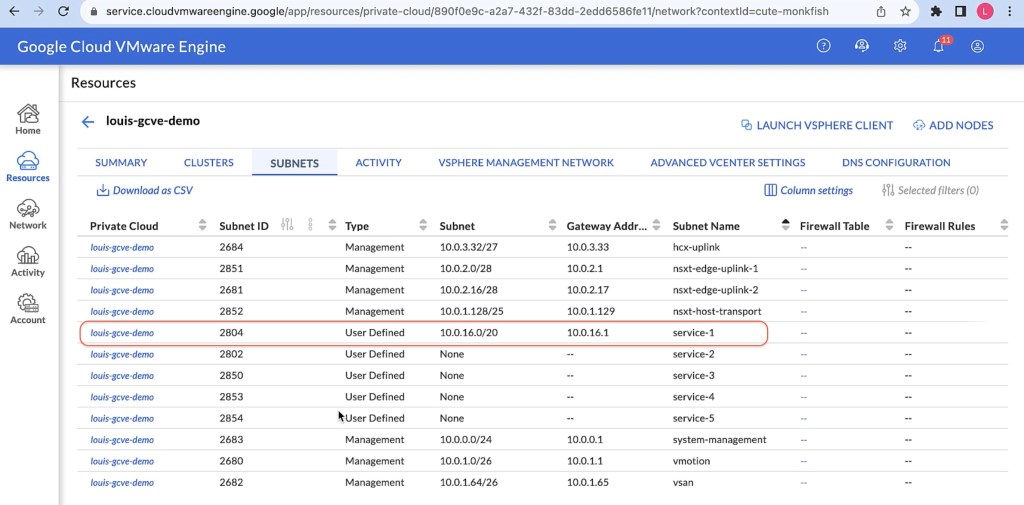
I assigned the “10.0.16.0/20” CIDR to service-1 subnet in GCVE. (The first usable address will become the gateway address)
Mounting NFS Datastores to a GCVE Cluster
To mount Filestore to a GCVE cluster, please note that currently this task cannot be performed through the self-service interface. You will need to reach out to Google support by filing a support ticket. Kindly provide them with the necessary information and they will assist you in completing the task successfully.
below is the sample information you may need to provide in the support ticket:
vCenter Server FQDN: vcsa-208856.e2422918.asia-northeast1.gve.goog
Private Cloud Name: louis-gcve-demo
Cluster Name: cluster
NFS Server type: Filestore
NFS Server IP and Path: 192.168.0.2:/gcve_filestore_ds1
Name of service subnet: service-1
VLAN of service subnet: 2804
Storage network CIDR: 10.0.16.0/20
GW IP: 10.0.16.1
Review the task
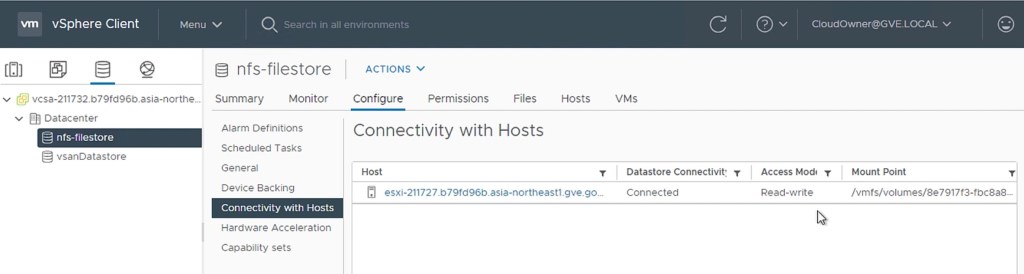
After Google Support completed the setup, you can check whether the Filestore file has been mounted in the GCVE cluster.

Create VM in Filestore NFS
Once the datastores are mounted and available, you can use vCenter UI to provision VMs against the external datastores, view metrics, and view logs related to I/O operations performed against external datastores.


You can also perform the storage vmotion action.
Summary
There are several reasons why you might want to use Filestore NFS as GCVE’s external datastore for ESXi:
- Performance: Filestore is a high-performance, scalable, and durable storage service that can provide good performance for tier-2 or tier-3 application workload.
- Security: Filestore is a secure storage service that offers a variety of features to help protect your data, such as encryption at rest and in transit, and role-based access control (RBAC).
- Simplicity: Filestore is a simple to use storage cloud managed service that offers a variety of features to make it easy to manage your data, such as snapshots, replication, and disaster recovery.
- Cost-effectiveness: Filestore is a cost-effective storage service that offers a variety of pricing options to fit your budget.
Notes
Video link: Use Google Cloud Filestore as external datastores for VMware ESXi hosts in Google Cloud VMware Engine